| CONDENSED MATTER: ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE, ELECTRICAL, MAGNETIC, AND OPTICAL PROPERTIES |
 |
|

|
|
|
New Superconductivity Dome in LaFeAsO1−xFx Accompanied by Structural Transition |
| YANG Jie1, ZHOU Rui1, WEI Lin-Lin1, YANG Huai-Xin1, LI Jian-Qi1, ZHAO Zhong-Xian1, ZHENG Guo-Qing1,2** |
1Institute of Physics and Beijing National Laboratory for Condensed Matter Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190
2Department of Physics, Okayama University, Okayama 700-8530, Japan |
|
| Cite this article: |
|
YANG Jie, ZHOU Rui, WEI Lin-Lin et al 2015 Chin. Phys. Lett. 32 107401 |
|
|
|
|
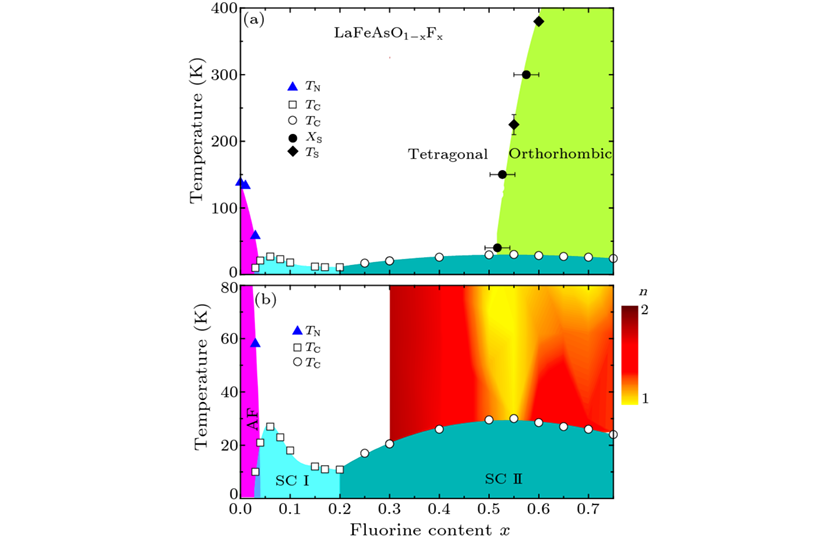
Abstract High-temperature superconductivity is often found in the vicinity of antiferromagnetism. This is also true in LaFeAsO1−xFx (x≤0.2) and many other iron-based superconductors, which leads to proposals that superconductivity is mediated by fluctuations associated with the nearby magnetism. Here we report the discovery of a new superconductivity dome without low-energy magnetic fluctuations in LaFeAsO1−xFx with 0.25≤x≤0.75, where the maximal critical temperature Tc at xopt=0.5–0.55 is even higher than that at x ≤0.2. By nuclear magnetic resonance and transmission electron microscopy, we show that a C4 rotation symmetry-breaking structural transition takes place for x>0.5 above Tc. Our results point to a new paradigm of high temperature superconductivity.
|
|
Received: 31 August 2015
Published: 30 October 2015
|
|
| PACS: |
74.25.nj
|
(Nuclear magnetic resonance)
|
| |
74.70.Xa
|
(Pnictides and chalcogenides)
|
| |
76.60.-k
|
(Nuclear magnetic resonance and relaxation)
|
| |
74.25.Ha
|
(Magnetic properties including vortex structures and related phenomena)
|
|
|
|
|
|
[1] Lee P A, Nagaosa N and Wen X G 2006 Rev. Mod. Phys. 78 17
[2] Mathur N D et al 1998 Nature 394 39
[3] Kamihara Y, Watanabe T, Hirano M and Hosono H 2008 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130 3296
[4] Ren Z A et al 2008 Chin. Phys. Lett. 25 2215
[5] Rotter M, Tegel M and Johrendt D 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 107006
[6] Sefat A S et al 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 117004
[7] Zhou R et al 2013 Nat. Commun. 4 2265
[8] Ren Z A et al 2008 Europhys. Lett. 83 17002
[9] Ning F L et al 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 037001
[10] Oka T et al 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 047001
[11] Li Z et al 2011 Phys. Rev. B 83 140506(R)
[12] Mazin I I, Singh D J, Johannes M D and Du M H 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 057003
[13] Kuroki K et al 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 087004
[14] Graser S et al 2010 Phys. Rev. B 81 214503
[15] Luetkens H et al 2009 Nat. Mater. 8 305
[16] Lu W et al 2008 Solid State Commun. 148 168
[17] Iimura S et al 2012 Nat. Commun. 3 943
[18] Narath A 1967 Phys. Rev. 162 320
[19] More data will be presented in a separate work.
[20] Matano K et al 2008 Europhys. Lett. 83 57001
[21] Abragam A 1961 The Principles of Nuclear Magnetism (Oxford: Oxford University Press)
[22] Fu M et al 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 247001
[23] Ma C et al 2008 Europhys. Lett. 84 47002
[24] de la Cruz C et al 2008 Nature 453 899
[25] Chu J H et al 2010 Science 329 824
[26] Fernandes R M, Chubukov A V and Schmalian J 2014 Nat. Phys. 10 97
[27] Fernandes R M, Bohmer A E, Meingast C and Schmalian J 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 111 137001
[28] Nakai Y, Kitagawa S and Ishida K 2009 New J. Phys. 11 045004
[29] Kontani H and Onari S 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 157001
[30] Chen C C et al 2010 Phys. Rev. B 82 100504
[31] Lee C C, Yin W G and Ku W 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 267001
[32] Lv W C, Wu J S and Phillips P 2009 Phys. Rev. B 80 224506
[33] Yamase H and Zeyher R 2013 Phys. Rev. B 88 180502(R)
[34] Hertz J A 1976 Phys. Rev. B 14 1165
[35] Moriya T 1991 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 100 261
[36] Yuan H Q et al 2003 Science 302 2104
[37] Hiraishi M et al 2014 Nat. Phys. 10 300 |
|
Viewed |
|
|
|
Full text
|
|
|
|
|
Abstract
|
|
|
|
|