| CONDENSED MATTER: ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE, ELECTRICAL, MAGNETIC, AND OPTICAL PROPERTIES |
 |
|

|
|
|
The 20-nm Skyrmion Generated at Room Temperature by Spin-Orbit Torques |
| Jiahao Liu1,2,3†, Zidong Wang1,2†, Teng Xu1,2, Hengan Zhou1,2, Le Zhao1,2, Soong-Guen Je4,5, Mi-Young Im4, Liang Fang3, and Wanjun Jiang1,2* |
1State Key Laboratory of Low-Dimensional Quantum Physics and Department of Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
2Frontier Science Center for Quantum Information, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
3Institute for Quantum Information & State Key Laboratory of High Performance Computing, College of Computer, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
4Center for X-ray Optics, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Cyclotron Road, Berkeley, CA 94720, USA
5Department of Physics, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, 61186, Republic of Korea
|
|
| Cite this article: |
|
Jiahao Liu, Zidong Wang, Teng Xu et al 2022 Chin. Phys. Lett. 39 017501 |
|
|
|
|
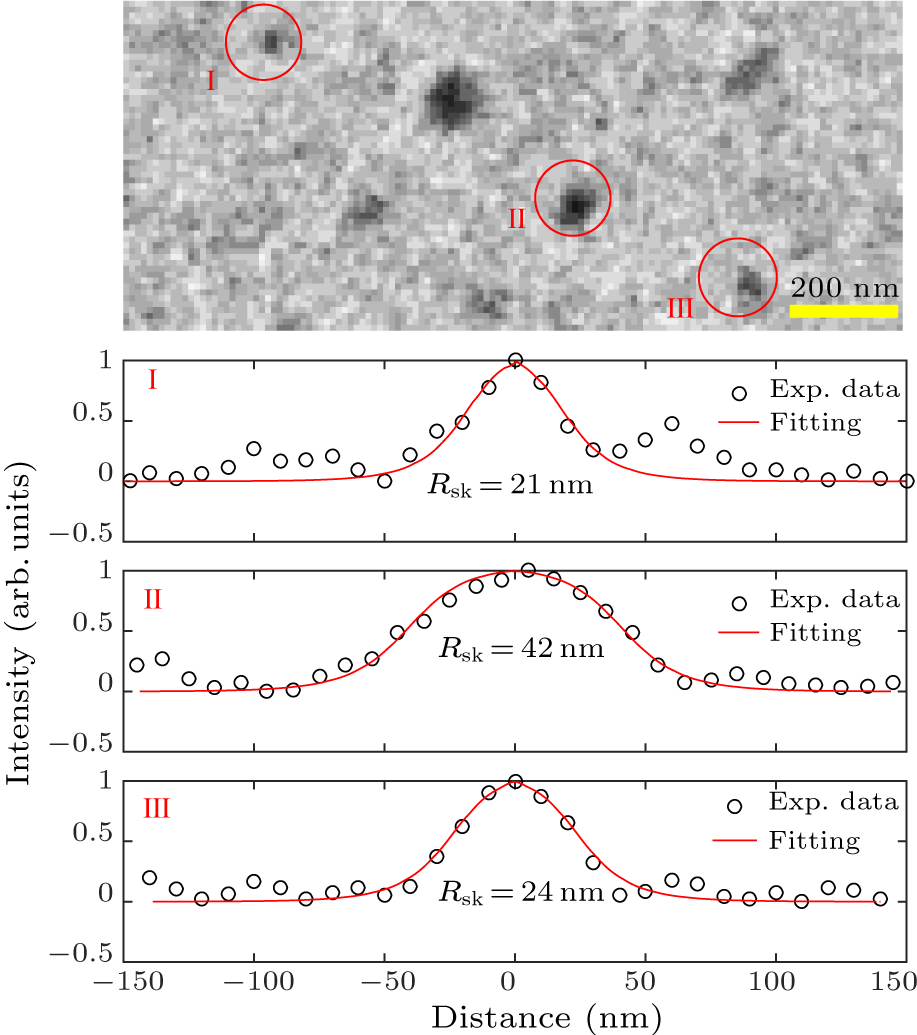
Abstract The discovery of magnetic skyrmions provides a promising pathway for developing functional spintronic memory and logic devices. Towards the future high-density memory application, nanoscale skyrmions with miniaturized diameters, ideally down to 20 nm are required. Using x-ray magnetic circular dichroism transmission microscopy, nanoscale skyrmions are observed in the [Pt/Co/Ir]$_{15}$ multilayer at room temperature. In particular, small skyrmions with minimum diameters approaching 20 nm could be generated by the current-induced spin-orbit torques. Through implementing material specific parameters, the dynamic process of skyrmion generation is further investigated by performing micromagnetic simulations. According to the simulation results, we find that both the tube-like Néel-type skyrmions and the bobber-like Néel-type skyrmions can be electrically generated. In particular, the size of the bobber-like Néel-type skyrmions can be effectively reduced by the spin-orbit torques, which leads to the formation of 20 nm Néel-type skyrmions. Our findings could be important for understanding the formation dynamics of nanoscale Néel-type spin textures, skyrmions and bobber in particular, which could also be useful for promoting nanoscale skyrmionic memories and logic devices.
|
|
Received: 02 November 2021
Express Letter
Published: 13 December 2021
|
|
| PACS: |
75.70.Cn
|
(Magnetic properties of interfaces (multilayers, superlattices, heterostructures))
|
| |
75.70.Tj
|
(Spin-orbit effects)
|
| |
75.78.Cd
|
(Micromagnetic simulations ?)
|
| |
75.70.Kw
|
(Domain structure (including magnetic bubbles and vortices))
|
| |
12.39.Dc
|
(Skyrmions)
|
|
|
|
|
|
| [1] | Bogdanov A and Hubert A 1994 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 138 255 |
| [2] | Bogdanov A N and Rößler U K 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 87 037203 |
| [3] | Fert A, Reyren N, and Cros V 2017 Nat. Rev. Mater. 2 17031 |
| [4] | Zang J et al. 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 107 136804 |
| [5] | Nagaosa N and Tokura Y 2013 Nat. Nanotechnol. 8 899 |
| [6] | Koshibae W et al. 2015 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 54 053001 |
| [7] | Chen G et al. 2015 Appl. Phys. Lett. 106 242404 |
| [8] | Braun H B 2012 Adv. Phys. 61 1 |
| [9] | Buettner F et al. 2015 Nat. Phys. 11 225 |
| [10] | Yang S H et al. 2021 Nat. Rev. Phys. 3 328 |
| [11] | Gobel B, Mertig I, and Tretiakov O A 2021 Phys. Rep. 895 1 |
| [12] | Back C et al. 2020 J. Phys. D 53 363001 |
| [13] | Everschor-Sitte K et al. 2018 J. Appl. Phys. 124 240901 |
| [14] | Skyrme T H R 1961 Proc. R. Soc. A 262 237 |
| [15] | Bogdanov N Y and Yablonskii D A 1989 Sov. Phys.-JETP 68 101 |
| [16] | Huang S X and Chien C L 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 267201 |
| [17] | Yu X Z et al. 2010 Nature 465 901 |
| [18] | Shibata K et al. 2013 Nat. Nanotechnol. 8 723 |
| [19] | Ritz R et al. 2013 Nature 497 231 |
| [20] | Neubauer A et al. 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 102 186602 |
| [21] | Pappas C et al. 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 102 197202 |
| [22] | Tonomura A et al. 2012 Nano Lett. 12 1673 |
| [23] | Yu X Z et al. 2013 Nano Lett. 13 3755 |
| [24] | Du H F et al. 2014 Nano Lett. 14 2026 |
| [25] | Jonietz F et al. 2010 Science 330 1648 |
| [26] | Kindervater J et al. 2019 Phys. Rev. X 9 041059 |
| [27] | Heinze S et al. 2011 Nat. Phys. 7 713 |
| [28] | Romming N et al. 2013 Science 341 636 |
| [29] | Emori S et al. 2013 Nat. Mater. 12 611 |
| [30] | Boulle O et al. 2016 Nat. Nanotechnol. 11 449 |
| [31] | DeRosa M C et al. 2010 Nat. Nanotechnol. 5 91 |
| [32] | Pizzini S et al. 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 113 047203 |
| [33] | Jiang W et al. 2017 Phys. Rep. 704 1 |
| [34] | Dupe B et al. 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 11779 |
| [35] | Woo S et al. 2016 Nat. Mater. 15 501 |
| [36] | Jiang W et al. 2015 Science 349 283 |
| [37] | Li W et al. 2019 Adv. Mater. 31 1807683 |
| [38] | Moreau-Luchaire C et al. 2016 Nat. Nanotechnol. 11 444 |
| [39] | Legrand W et al. 2017 Nano Lett. 17 2703 |
| [40] | Jiang W et al. 2019 Phys. Rev. B 99 104402 |
| [41] | Pollard S D et al. 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 14761 |
| [42] | Soumyanarayanan A et al. 2017 Nat. Mater. 16 898 |
| [43] | Raju M et al. 2019 Nat. Commun. 10 696 |
| [44] | Guang Y et al. 2020 Nat. Commun. 11 949 |
| [45] | Zhou H A et al. 2021 Adv. Funct. Mater. 31 2104426 |
| [46] | Caretta L et al. 2018 Nat. Nanotechnol. 13 1154 |
| [47] | Fert A, Cros V, and Sampaio J 2013 Nat. Nanotechnol. 8 152 |
| [48] | Parkin S S P, Hayashi M, and Thomas L 2008 Science 320 190 |
| [49] | Iwasaki J, Mochizuki M, and Nagaosa N 2013 Nat. Nanotechnol. 8 742 |
| [50] | Sampaio J et al. 2013 Nat. Nanotechnol. 8 839 |
| [51] | Ding J J, Yang X F, and Zhu T 2015 J. Phys. D 48 115004 |
| [52] | Schulz T et al. 2012 Nat. Phys. 8 301 |
| [53] | Wang Z et al. 2020 Nat. Electron. 3 672 |
| [54] | Sinova J et al. 2015 Rev. Mod. Phys. 87 1213 |
| [55] | Yu G Q et al. 2016 Nano Lett. 16 1981 |
| [56] | Tomasello R et al. 2018 Phys. Rev. B 97 060402(R) |
| [57] | Lemesh I et al. 2018 Adv. Mater. 30 1805461 |
| [58] | Landau L D and Lifshitz E M 1935 Phys. Z. Sowjetunion 8 153 |
| [59] | Buttner F et al. 2017 Nat. Nanotechnol. 12 1040 |
| [60] | Rohart S and Thiaville A 2013 Phys. Rev. B 88 184422 |
| [61] | Bernand-Mantel A et al. 2020 Phys. Rev. B 101 045416 |
| [62] | Zheng F et al. 2018 Nat. Nanotechnol. 13 451 |
| [63] | Ran K et al. 2021 Phys. Rev. Lett. 126 017204 |
| [64] | Zhu J et al. 2021 Sci. Chin. Phys. Mech. & Astron. 64 227511 |
| [65] | Gong Z Z et al. 2021 Phys. Rev. B 104 L100412 |
|
|
Viewed |
|
|
|
Full text
|
|
|
|
|
Abstract
|
|
|
|
|