| CONDENSED MATTER: ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE, ELECTRICAL, MAGNETIC, AND OPTICAL PROPERTIES |
 |
|

|
|
|
Evidence for Multiple Underlying Fermi Surface and Isotropic Energy Gap in the Cuprate Parent Compound Ca$_2$CuO$_2$Cl$_2$ |
| Cheng Hu1,2, Jian-Fa Zhao1,2, Ying Ding1,2, Jing Liu1,2, Qiang Gao1,2, Lin Zhao1, Guo-Dong Liu1, Li Yu1, Chang-Qing Jin1,2,4, Chuang-Tian Chen3, Zu-Yan Xu3, Xing-Jiang Zhou1,2,4** |
1Beijing National Laboratory for Condensed Matter Physics, Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190
2University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049
3Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190
4Collaborative Innovation Center of Quantum Matter, Beijing 100871 |
|
| Cite this article: |
|
Cheng Hu, Jian-Fa Zhao, Ying Ding et al 2018 Chin. Phys. Lett. 35 067403 |
|
|
|
|
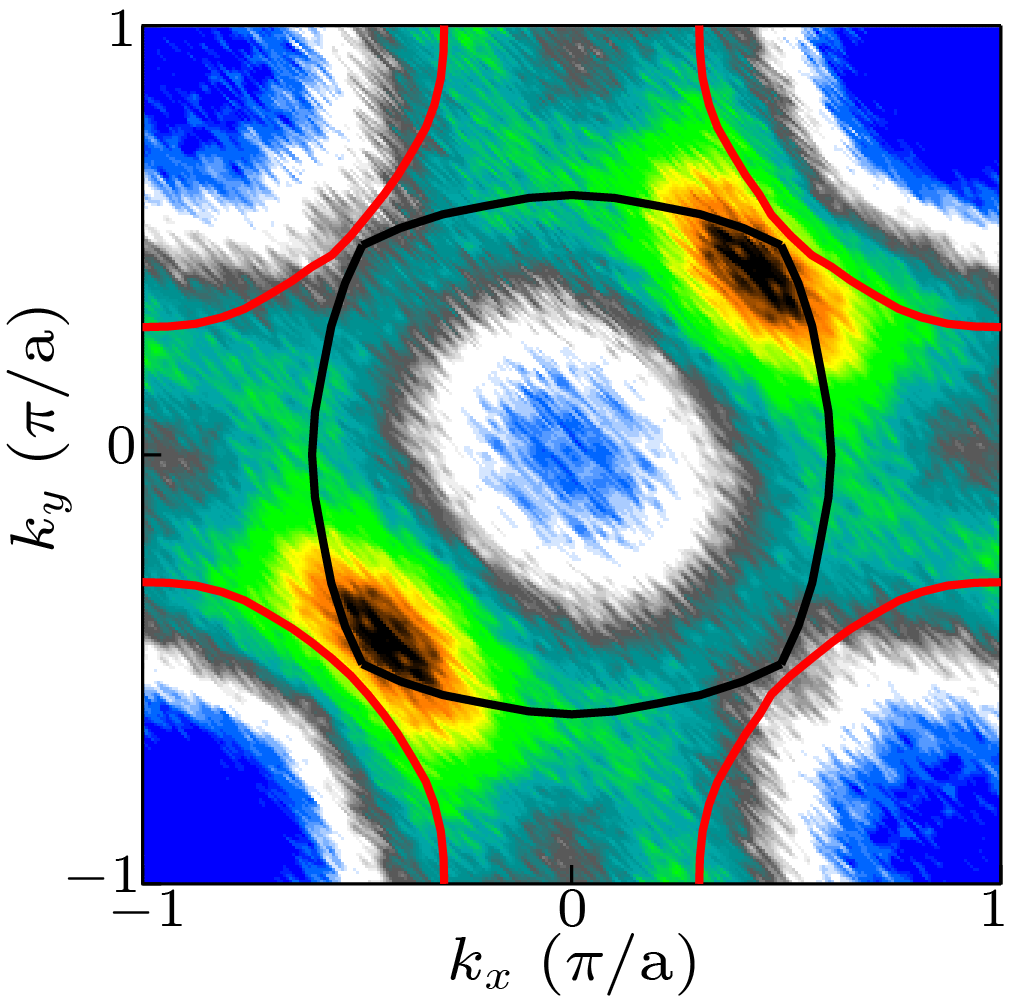
Abstract The parent compounds of the high-temperature cuprate superconductors are Mott insulators. It has been generally agreed that understanding the physics of the doped Mott insulators is essential to understanding the mechanism of high temperature superconductivity. A natural starting point is to elucidate the basic electronic structure of the parent compound. Here we report comprehensive high resolution angle-resolved photoemission measurements on Ca$_2$CuO$_2$Cl$_2$, a Mott insulator and a prototypical parent compound of the cuprates. Multiple underlying Fermi surface sheets are revealed for the first time. The high energy waterfall-like band dispersions exhibit different behaviors near the nodal and antinodal regions. Two distinct energy scales are identified: a d-wave-like low energy peak dispersion and a nearly isotropic lower Hubbard band gap. These observations provide new information of the electronic structure of the cuprate parent compound, which is important for understanding the anomalous physical properties and superconductivity mechanism of the high temperature cuprate superconductors.
|
|
Received: 20 May 2018
Published: 23 May 2018
|
|
| PACS: |
74.72.Cj
|
(Insulating parent compounds)
|
| |
71.18.+y
|
(Fermi surface: calculations and measurements; effective mass, g factor)
|
| |
74.25.Jb
|
(Electronic structure (photoemission, etc.))
|
| |
79.60.-i
|
(Photoemission and photoelectron spectra)
|
| |
71.20.-b
|
(Electron density of states and band structure of crystalline solids)
|
|
|
| Fund: Supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFA0300300), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11334010 and 11534007), the National Basic Research Program of China (2015CB921000), and the Strategic Priority Research Program (B) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB07020300). |
|
|
|
|
Viewed |
|
|
|
Full text
|
|
|
|
|
Abstract
|
|
|
|
|