| FUNDAMENTAL AREAS OF PHENOMENOLOGY(INCLUDING APPLICATIONS) |
 |
|

|
|
|
Prediction of Thermal Conductance of Complex Networks with Deep Learning |
| Changliang Zhu1, Xiangying Shen1*, Guimei Zhu2*, and Baowen Li1,2,3,4 |
1Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China
2School of Microelectronics, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China
3Department of Physics, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China
4Shenzhen International Quantum Academy, Shenzhen 518017, China
|
|
| Cite this article: |
|
Changliang Zhu, Xiangying Shen, Guimei Zhu et al 2023 Chin. Phys. Lett. 40 124402 |
|
|
|
|
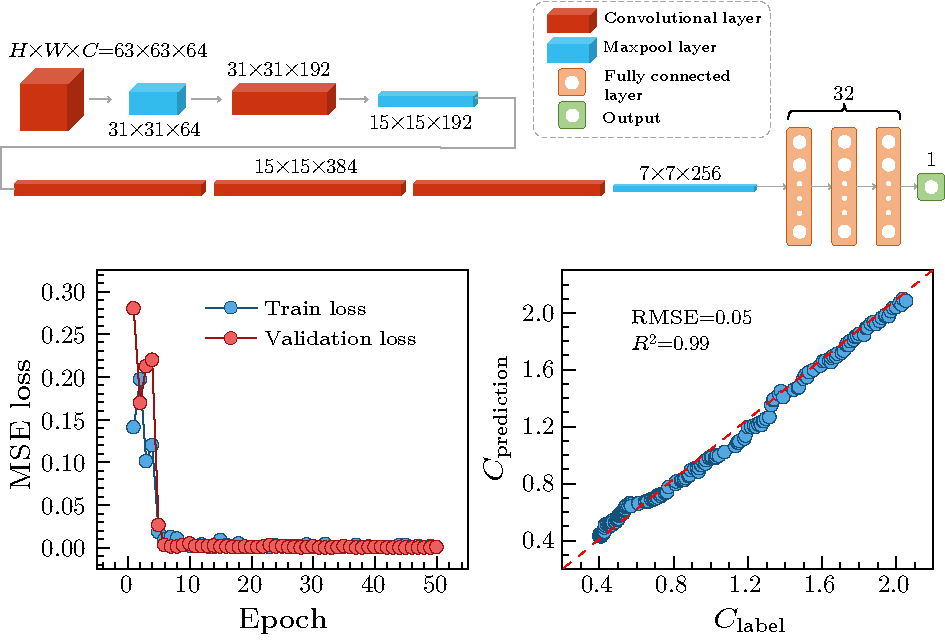
Abstract Predicting thermal conductance of complex networks poses a formidable challenge in the field of materials science and engineering. This challenge arises due to the intricate interplay between the parameters of network structure and thermal conductance, encompassing connectivity, network topology, network geometry, node inhomogeneity, and others. Our understanding of how these parameters specifically influence heat transfer performance remains limited. Deep learning offers a promising approach for addressing such complex problems. We find that the well-established convolutional neural network models AlexNet can predict the thermal conductance of complex network efficiently. Our approach further optimizes the calculation efficiency by reducing the image recognition in consideration that the thermal transfer is inherently encoded within the Laplacian matrix. Intriguingly, our findings reveal that adopting a simpler convolutional neural network architecture can achieve a comparable prediction accuracy while requiring less computational time. This result facilitates a more efficient solution for predicting the thermal conductance of complex networks and serves as a reference for machine learning algorithm in related domains.
|
|
Received: 19 October 2023
Express Letter
Published: 22 November 2023
|
|
| PACS: |
07.05.Mh
|
(Neural networks, fuzzy logic, artificial intelligence)
|
| |
89.75.Fb
|
(Structures and organization in complex systems)
|
| |
89.75.-k
|
(Complex systems)
|
| |
44.10.+i
|
(Heat conduction)
|
|
|
|
|
|
| [1] | Dorogovtsev S N, Goltsev A V, and Mendes J F 2008 Rev. Mod. Phys. 80 1275 |
| [2] | Yan H, Park S H, Finkelstein G, Reif J H, and LaBean T H 2003 Science 301 1882 |
| [3] | Liu D G, Park S H, Reif J H, and LaBean T H 2004 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101 717 |
| [4] | Yin P, Hariadi R F, Sahu S, Choi H M, Park S H, LaBean T H, and Reif J H 2008 Science 321 824 |
| [5] | Wang S, Zeng C, Zhu G, Wang H, and Li B 2023 Phys. Rev. Res. 5 043009 |
| [6] | Shen X Y, Zhu G M, and Li B W 2023 Sci. Chin. Phys. Mech. & Astron. 66 260501 |
| [7] | Shen X Y, Fang C C, Jin Z P, Tong H, Tang S X, Shen H C, Xu N, Lo J H Y, Xu X L, and Xu L 2021 Nat. Mater. 20 1635 |
| [8] | Xi Q, Zhong J X, He J X, Xu X F, Nakayama T, Wang Y, Liu J, Zhou J, and Li B W 2020 Chin. Phys. Lett. 37 104401 |
| [9] | Newman M E and Park J 2003 Phys. Rev. E 68 036122 |
| [10] | Albert R, Jeong H, and Barabási A L 2000 Nature 406 378 |
| [11] | Laughlin S B and Sejnowski T J 2003 Science 301 1870 |
| [12] | Tian C H, Cao L, Bi H J, Xu K, and Liu Z H 2018 Nonlinear Dyn. 93 1695 |
| [13] | Song Y J, Garcia R M, Dorin R M, Wang H, Qiu Y, Coker E N, Steen W A, Miller J E, and Shelnutt J A 2007 Nano Lett. 7 3650 |
| [14] | Hu L, Hecht D, and Grüner G 2004 Nano Lett. 4 2513 |
| [15] | Hecht D, Hu L, and Grüner G 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett. 89 133112 |
| [16] | Rauber M, Alber I, Müller S, Neumann R, Picht O, Roth C, Schökel A, Toimil-Molares M E, and Ensinger W 2011 Nano Lett. 11 2304 |
| [17] | van de Groep J, Spinelli P, and Polman A 2012 Nano Lett. 12 3138 |
| [18] | Xiong K Z, Liu Z H, Zeng C H, and Li B W 2020 Natl. Sci. Rev. 7 270 |
| [19] | Xiong K Z, Yan Z X, Xie Y, Wang Y X, Zeng C H, and Liu Z H 2022 Nonlinear Dyn. 110 2771 |
| [20] | Xiong K Z, Zeng C H, and Liu Z H 2018 Nonlinear Dyn. 94 3067 |
| [21] | Xiong K Z, Zeng C H, Liu Z H, and Li B W 2018 Phys. Rev. E 98 022115 |
| [22] | Xiong K Z, Zhou J, Tang M, Zeng C H, and Liu Z H 2018 Phys. Rev. E 98 062144 |
| [23] | Xiong K Z, Zhou M, Liu W, Zeng C H, and Yan Z X 2023 Chaos 33 083144 |
| [24] | Dhar A 2008 Adv. Phys. 57 457 |
| [25] | Li N B, Ren J, Wang L, Zhang G, Hänggi P, and Li B W 2012 Rev. Mod. Phys. 84 1045 |
| [26] | Cahill D G, Ford W K, Goodson K E, Mahan G D, Majumdar A, Maris H J, Merlin R, and Phillpot S R 2003 J. Appl. Phys. 93 793 |
| [27] | Kumar S, Murthy J, and Alam M 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 95 066802 |
| [28] | Pop E, Mann D, Cao J, Wang Q, Goodson K, and Dai H 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 95 155505 |
| [29] | Boccaletti S, Latora V, Moreno Y, Chavez M, and Hwang D U 2006 Phys. Rep. 424 175 |
| [30] | Albert R and Barabási A L 2002 Rev. Mod. Phys. 74 47 |
| [31] | Watts D J and Strogatz S H 1998 Nature 393 440 |
| [32] | Oliveira C L, Morais P A, Moreira A A, and Andrade J S 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 112 148701 |
| [33] | Xiong K Z, Yan Z X, Xie Y, and Liu Z H 2021 Sci. Rep. 11 5501 |
| [34] | Zhang Z W, Yang S, Wu Y H, Liu C X, Han Y M, Lee C H, Sun Z, Li G J, and Zhang X 2020 Chin. Phys. Lett. 37 018401 |
| [35] | Ouyang Y L, Zhang Z W, Yu C Q, He J, Yan G, and Chen J 2020 Chin. Phys. Lett. 37 126301 |
| [36] | Zhang Y C, Blattner M, and Yu Y K 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 99 154301 |
| [37] | Liu Z H, Wu X, Yang H J, Gupte N, and Li B W 2010 New J. Phys. 12 023016 |
|
|
Viewed |
|
|
|
Full text
|
|
|
|
|
Abstract
|
|
|
|
|