| FUNDAMENTAL AREAS OF PHENOMENOLOGY(INCLUDING APPLICATIONS) |
 |
|

|
|
|
Breakdown of Energy Equipartition in Vibro-Fluidized Granular Media in Micro-Gravity |
| CHEN Yan-Pei1,2, Pierre Evesque2, HOU Mei-Ying1** |
1Key Laboratory of Soft Matter Physics, Beijing National Laboratory for Condensed Matter Physics, Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190
2Lab MSSMat, Ecole Centrale de Paris, UMR 8579 CNRS, 92295 Chatenay-Malabry Cedex, France |
|
| Cite this article: |
|
CHEN Yan-Pei, Pierre Evesque, HOU Mei-Ying 2012 Chin. Phys. Lett. 29 074501 |
|
|
|
|
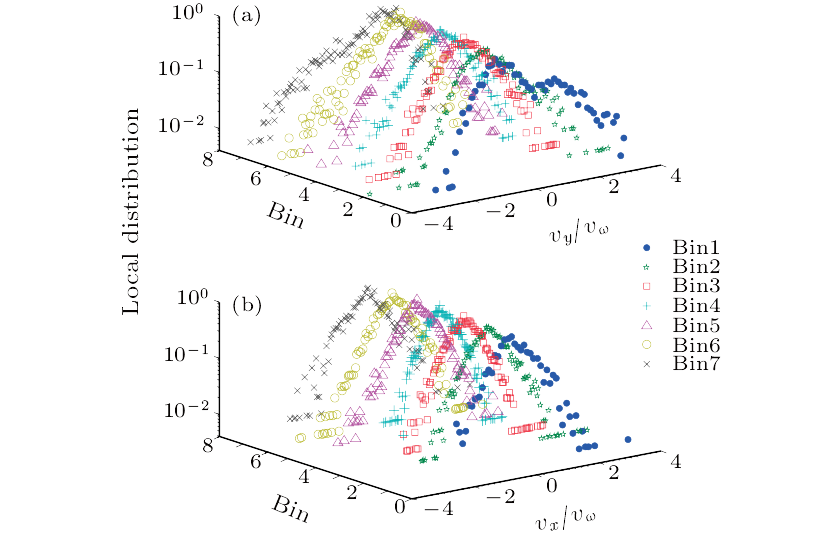
Abstract We present a micro-gravity experimental study of intermediate number density vibro-fluidized inelastic spheres in a rectangular container. Local velocity distributions are investigated, and are found to deviate measurably from a symmetric distribution for the velocity component of the vibrating direction when dividing particles along the vibration direction into several bins. This feature does not exist in the molecular gas. We further study the hydrodynamic profiles of pressures p and temperatures T in positive and negative components, such as py+ and py− and Ty+ and Ty−, in accordance with the sign of velocity components of the vibrating direction. Along vibration direction, granular media are found to be not only inhomogeneous and anisotropic, but also different greatly in positive and negative components. Energy equipartition breaks down in this case.
|
|
Received: 20 June 2012
Published: 29 July 2012
|
|
| PACS: |
45.70.-n
|
(Granular systems)
|
| |
51.30.+i
|
(Thermodynamic properties, equations of state)
|
| |
51.10.+y
|
(Kinetic and transport theory of gases)
|
|
|
|
|
|
[1] Grossman E L, Zhou T and Ben-Naim E 1997 Phys. Rev. E 55 4200
[2] Herbst O, Müller P, Otto M and Zippelius A 2004 Phys. Rev. E 70 051313
[3] Sergei E E and Pöchel T 1997 J. Stat. Phys. 86 1385
[4] Olafsen J S and Urbach J S 1999 Phys. Rev. E 60 R2468
[5] Olafsen J S and Urbach J S 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 81 4369
[6] Rouyer F and Menon N F 2000 Phys. Rev. Lett. 85 3676
[7] Kudrolli A, Wolpert M and Gollub J P 1997 Phys. Rev. Lett. 78 1383
[8] Losert W, Cooper W D G, Delour J, Kudrolli A and Gollub J P 1999 Chaos 9 682
[9] Hou M, Liu R, Zhai G, Sun Z and Lu K 2008 Micrograv. Sci. Technol. 20 73
[10] Noije T P C and Ernst M H 1998 Granul. Matter 1 57
[11] Brey J J, Ruiz-Montero M J and Cubero D 1996 Phys. Rev. E 54 3664
[12] Huthmann M, Orza J A and Brito R 2000 Granul. Matter 2 189
[13] Evesque P 2002 Poudres Grains 13 20
Evesque P 2002 Poudres Grains 13 40
[14] Evesque P 2005 Poudres Grains 15 1
Evesque P 2005 Poudres Grains 15 18
[15] Liu R, Hou M and Evesque P 2009 Poudres Grains 17 1
[16] Brey J J, Ruiz-Montero M J and Moreno F 2000 Phys. Rev. E 62 5339
[17] Herbst O, Muller P and Zippelius A 2005 Phys. Rev. E 72 041303
[18] Leconte M, Garrabos Y, Palencia F, Lecoutre C, Evesque P and Beysens D 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett. 89 243518
[19] Brilliantov N V and Pöschel T 2004 Kinetic Theory of Granular Gases ( New York: Oxford University)
[20] Brey J J and Cubero D 1998 Phys. Rev. E 57 2019
[21] Barrat A and Trizac E 2002 Phys. Rev. E 66 051303
[22] McNamara S and Luding S 1998 Phys. Rev. E 58 813
[23] van der Meer D and Reimann P 2006 Europhys. Lett. 74 384 |
|
Viewed |
|
|
|
Full text
|
|
|
|
|
Abstract
|
|
|
|
|